Since the arrival of Iron Man, Marvel Studios has built a major platform for distributing profitable movies. In the summer of 2015, they introduced a new superhero called Ant-Man. In its opening weekend, the movie earned $177 million at the domestic box office. Forbes Magazine reported the movie actually made more initial money than previous films like Captain America: The First Avenger.
However, the most impressive feat the film pulled off was becoming the cheapest film to date in comparison to previous Marvel Studios productions. One of the biggest blockbusters of the year cost $130 million to make and a majority of the budget was spent in one city: Atlanta, Georgia.
Tax incentives and more job opportunities continue to shift the established economic model of strictly Hollywood filmmaking. The increasing number of runaway productions, or movies filmed in other states for economic reasons, has given other states some advantages and disadvantages in the lucrative film business.
Inexpensive filming locations, like Atlanta, are fast becoming a favored spots to make a movie, but the city also has the potential to become the new entertainment capital of the United States.
Why did Georgia want a piece of the film industry pie?
Before the earliest introduction of tax incentive programs, films were made in locations outside of Hollywood for creative reasons. Some films and television programs today still follow this procedure, such as the HBO series Game of Thrones, which films in Ireland and Spain to reflect the locations in the original novels.
In 1997, everything changed when Canada introduced the Production Services Tax Credit program. According to the Department of Canadian Heritage, the program was designed to promote Canada as a less expensive place for film productions to take up shop. The Canadian government created a 16 percent tax credit to alleviate the expenses productions usually incur in Hollywood. Tax credits are tax incentives created by states and countries to remove a small amount of the income tax productions companies owe the state or country. As a result, Canada started looking like a cheaper place to invest in both television and film.
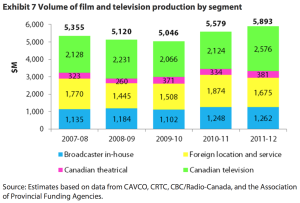 In the last several years, Canada has built a large repertoire of foreign film productions, with many coming from the United States. Between 2010 and 2011, about 33 percent of film and television production in Canada was through foreign production
In the last several years, Canada has built a large repertoire of foreign film productions, with many coming from the United States. Between 2010 and 2011, about 33 percent of film and television production in Canada was through foreign production
companies. Once the Canadian government started their program, runaway productions began to affect the United States.
A 1998 study conducted by the management-consulting firm Monitor Deloitte revealed 285 of the 1,075 films recorded for the study were economic runaways. Due to almost a third of productions moving out of state, the U.S. lost $10.3 billion, which combines the loss in direct production spending and the loss in spending and tax revenues.
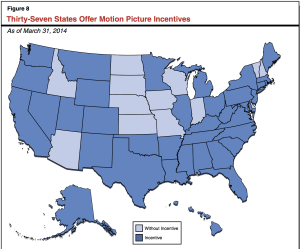
Today, 37 states including Georgia have similar tax incentive programs because of the growing fear of runaway productions in places like Canada. More states now compete to counter the massive success of their neighbor to the north. In a sense, Georgia began its own program about fifteen years ago because every other state had the same mentality: If Canada can have the same economic benefits of Hollywood in California, why can’t I?
(Courtesy: California Legislative Analyst’s Office)
A Brief History of the Georgia Film Tax Credit
Since the 1970s, Georgia has been the location for several movies, television shows and music videos. Famous films like Deliverance, Fried Green Tomatoes, Forrest Gump, and Remember The Titans all found their home in and around the state capital Atlanta. Although Georgia had a steady amount of film production for a number of years, it was not until 2001 when the state government became more interested in capitalizing on the filmmakers interested in heading south for cheaper production opportunities.
The Georgia General Assembly passed legislation in 2001 exempting the television and film companies from sales and use taxes on production expenses. This meant productions did not have to pay taxes on the film equipment they needed and bought in the state. In 2005, the creation of the Entertainment Industry Investment Act allowed out-of-state production companies to apply for a 9 percent base tax credit for productions over $500,000. The state income tax in 2005 was set at 35 percent, but with the 9 percent tax credit it meant larger productions only had to pay 26 percent. In addition, the law gave another 3 percent tax credit to filmmakers who spent money in poor and rural counties or on income paid to Georgia residents.
As film production declined in 2006 and more states like Louisiana and North Carolina began constructing their own incentives, then Georgia governor Sonny Perdue was quick to revise the law in 2008. He expanded the tax credit from 9 percent to 20 percent. Additional incentives included another 10 percent for placing a Georgia logo in the finished film. The potential to receive a 30 percent tax credit for working in Atlanta instead of Los Angeles started to become more lucrative for production companies.
Three Reasons Georgia has (arguably) the Best Tax Credits in the U.S.
1. Transferable Tax Credit – Georgia is one of 14 states who offer transferable tax credits, which allows production companies with tax credits exceeding their tax liability to sell the credits to other taxpayers. Since most productions companies coming from out of state do not have tax liability, tax credits in Georgia have a greater value.
2. Multi-Year Tax Credit – Georgia has a carry-forward period of up to five years for tax credits. This means production companies have up to five years to claim the tax credit against tax liability.
3. No Production Caps – Production companies can request unlimited tax off-set liability. This means Georgia has a better chance of attracting big-budget movies capable of bringing in large amounts of revenue.
Criticisms of the Georgia Film Tax Credit
This past summer, Georgia governor Nathan Deal announced film and television productions made $6 billion for the state during the fiscal year 2015. Some critics argue this number is inaccurate because the direct spending in Georgia this past year was $1.7 billion. The Atlanta-Journal Constitution reported in August the state economic development department uses a specific multiplier, 3.57, to estimate the economic impact of film production. Officials from the department said they were unsure of the credibility of the multiplier, even if it did supposedly quantify the revenue generated by production companies.
Another big issue in the film tax credit world is whether tax credits are a form of corporate welfare. Corporate welfare refers to a disproportionate amount of tax breaks given to corporations rather than groups in need of the money. The Tax Foundation, a non-partisan research group from Washington D.C., released a report in April 2015 saying state tax incentives actually cost states revenue and can increase taxes in other areas of their budgets.
Runaway production has also had huge impact on the people working in the film industry. As more production companies are making places like Georgia their home, more workers based in Los Angeles get hurt by the constant maneuvering of out-of-state production. However, the workers are trying to fight back. Last year, Variety reported Los Angeles-based visual effects artists launched a campaign to get the U.S. government to place a tax on countries taking away business by subsidizing labor costs. These actions indicate the constant traveling of film production workers has taken a toll. In the race to have the best tax incentives of any state, Georgia is also alienating some members of the industry with their lucrative tax credits.
Goodbye Hollywood, Hello Y’allywood
The film industry in Georgia continues to flourish today as more production companies decide to not only shoot movies, but also take up shop in Atlanta. Pinewood Studios Group, a multinational film facility company based out of the United Kingdom, opened Pinewood Atlanta Studios in 2014. It was the primary filming location for Ant-Man and, according to its website, will now serve as the filming location for the upcoming Captain America sequel.
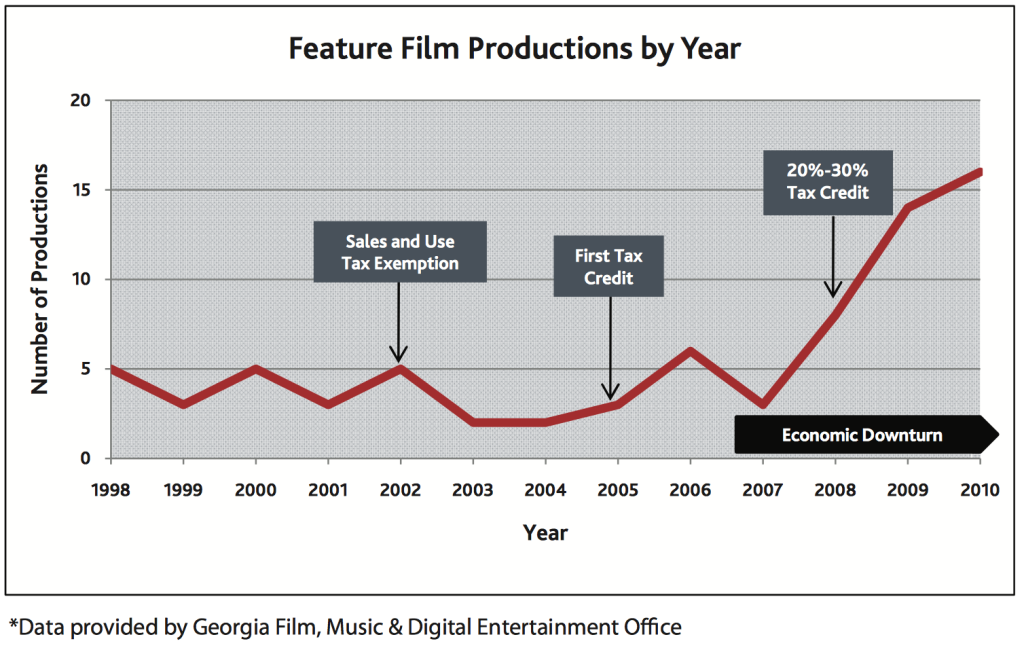
The sharp rise in the tax incentives has also had an equally dramatic effect on the number of productions. The chart above shows, between approximately 2003 and 2005, there were less than 5 film productions in the state. In a statement released by the commissioner of the Georgia Department of Economic Development in July 2015, the state had 42 productions filming at the same time. He argued more than 100 new businesses flocked to Georgia since the expansion of the tax credit in order to support the industry. Although the economic impact of film and television production appears to be heading in the right direction with greater job opportunities for multiple businesses, there are still major issues Georgia faces as it builds its identity as an entertainment powerhouse.
Issues Facing The Georgia Film Industry Part 1: Suitable Workforce
In June 2015, the Motion Picture Association of America reported the state film industry provides over 24,000 jobs and pays local workers over $1.68 billion in wages. In addition, the MPAA said the average salary for a worker in the industry is $84,000.
Well-paying jobs are bringing in a greater number of local people seeking employment, but the industry lacks the proper workforce to keep film production at a high standard. In the earlier days of the Georgia film incentive, the major challenge for the state was how to keep people within the industry to build their careers in Atlanta. Production companies would import people in from Los Angeles to do the work needed because Georgia did not have enough local citizens who had the skills needed to be successful in the industry. Today, Georgia continues to struggle with this problem. An NBC News article published in September revealed industry executives in Atlanta wanted to hire people from within the state, but instead were forced to look everywhere else to get the necessary workers.
However, recent events indicate Georgia may have found a solution: The Georgia Film Academy. The academy reflects a growing need for film industry training and education. According to the Atlanta Business Chronicle, Kennesaw State University professor Jeffrey Stepakoff was chosen to head the program, which will work in conjunction with university and technical college systems in the state. The academy will offer certification for entry level positions in the film industry in order to give people an opportunity to land a job with specialized skills. In addition, production and studio companies are taking notice of the new initiative. Pinewood Studios is the first major partner of the academy, which will give students the chance to get hands-on experience on real film sets as part of their classes.
How can Georgia measure job success in the film industry?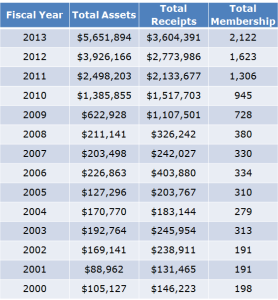
Georgia is a right-to-work state, which means any workers can work for a living with or without joining a union. However, in the last several years, the number of people joining film worker unions in Atlanta has grown dramatically. (U.S. Department of Labor) These numbers suggest a shifting trend in the industry from imported workers from the west coast to local workers with more expertise in film production.
Issues Facing The Georgia Film Industry Part 2: Competition
Another obstacle for the Georgia film industry remains the stiff competition with different states and Hollywood itself. A year ago, California governor Jerry Brown signed an expansion of the film and television tax credits. The main goal of the legislation was to triple the size of the tax credits to $330 million and reduce the amount of production that was leaving the state. In an interview with the Atlanta NPR station, the communications director for Los Angeles mayor Eric Garcetti explained how the employment gains in states like Georgia puts middle class jobs in California in danger.
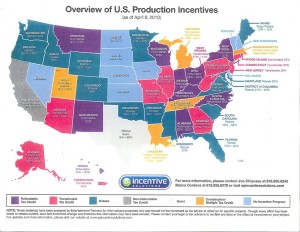 Other states, such as New York, New Mexico, and Louisiana, have similar ambitions to Georgia. They want a piece of the $57 billion dollar film production pie in the United States. In the state of New York, the tax incentives were raised to 30 percent in 2008. In New York City, the potential tax credit is now 35 percent, which is much higher than Georgia. In New Mexico, the tax credits sit at 25 percent, but the state established a Film Crew Advancement Program, which reimburses 50 percent of wages of local workers for hands-on training. Georgia will begin its own program, the Georgia Film Academy, in January 2016. Louisiana began offering refundable, permanent and transferable tax credits in 2002. Similar to Georgia, increased film production enabled the state to expand its infrastructure and labor force. Overall, Georgia faces stiff competition for film production from around the country. However, their goal of trying to become one of the top five film destinations in the country and the distinct perks of the tax credits compared to other states like California does give Georgia an edge over the competition.
Other states, such as New York, New Mexico, and Louisiana, have similar ambitions to Georgia. They want a piece of the $57 billion dollar film production pie in the United States. In the state of New York, the tax incentives were raised to 30 percent in 2008. In New York City, the potential tax credit is now 35 percent, which is much higher than Georgia. In New Mexico, the tax credits sit at 25 percent, but the state established a Film Crew Advancement Program, which reimburses 50 percent of wages of local workers for hands-on training. Georgia will begin its own program, the Georgia Film Academy, in January 2016. Louisiana began offering refundable, permanent and transferable tax credits in 2002. Similar to Georgia, increased film production enabled the state to expand its infrastructure and labor force. Overall, Georgia faces stiff competition for film production from around the country. However, their goal of trying to become one of the top five film destinations in the country and the distinct perks of the tax credits compared to other states like California does give Georgia an edge over the competition.
The Future of the Georgia Film Industry
Despite various roadblocks, the film industry in Georgia continues to expand to attract more people. There are several reasons why the film industry will remain vibrant in Georgia.
The construction of more film studios brings in more foot traffic to the area. According to the Atlanta Journal Constitution, close to 80 film industry companies relocated or expanded to Atlanta in the last six years. Several production companies and real estate developers have chosen Atlanta as their base of operations, including Jim Jacoby. He plans to build a 5 million square foot production facility catering to film, television, and video game development. The massive Atlanta Media and Campus and Studios would include sound stages, offices, and classrooms.
Financial stability of the state film industry will play a huge role in attracting more people to turn Atlanta into the new Hollywood. Some states, like California, expanded their tax credits, while others are now looking to eliminate incentives all together. In addition, the film industry could succeed because of the mass migration of several other businesses to the area. Service industries, such as tourism or catering, could see a large boost in profitability as the interest in films produced in Atlanta expands further.
State identity could be another reason why the film industry succeeds. Georgia has a variety of shooting locations needed for different films, whether its an urban or rural environment that would be needed. In addition, Atlanta is home to Hartsfield-Jackson International Airport, which holds the title of busiest airport in the world. The airport has direct flights between Los Angeles and Atlanta several times a day, making travel accommodations for the cast and crew of a film fairly easy.
Georgia is in the midst of a major shift in its emphasis on the entertainment industry, but the future looks bright for the state as it embraces more alternative methods to make it the Hollywood of the South.






 generation shift.
generation shift.