
(McKinsey Analysis)
The next time you are in a public place take a look around you. Nine out of ten people you see have just recently been on the internet. And among young adults ninety-nine out of every one hundred have recently been online. The internet has changed our lives in the way that we are able to do work, exchange and discover new ideas, socialize, and communicate with one another. However, it is not often that we think about the significance of this transformation in economics and how it can be used to measure economic growth.
Individuals from large enterprises, individual consumers, and small up and coming entrepreneurs all benefit from the enormous opportunities the internet has created such as building a competitive environment, boosting infrastructure and access, providing purchasing power, as well as nurturing human capital. In harmony these components have maximized economic growth and prosperity.
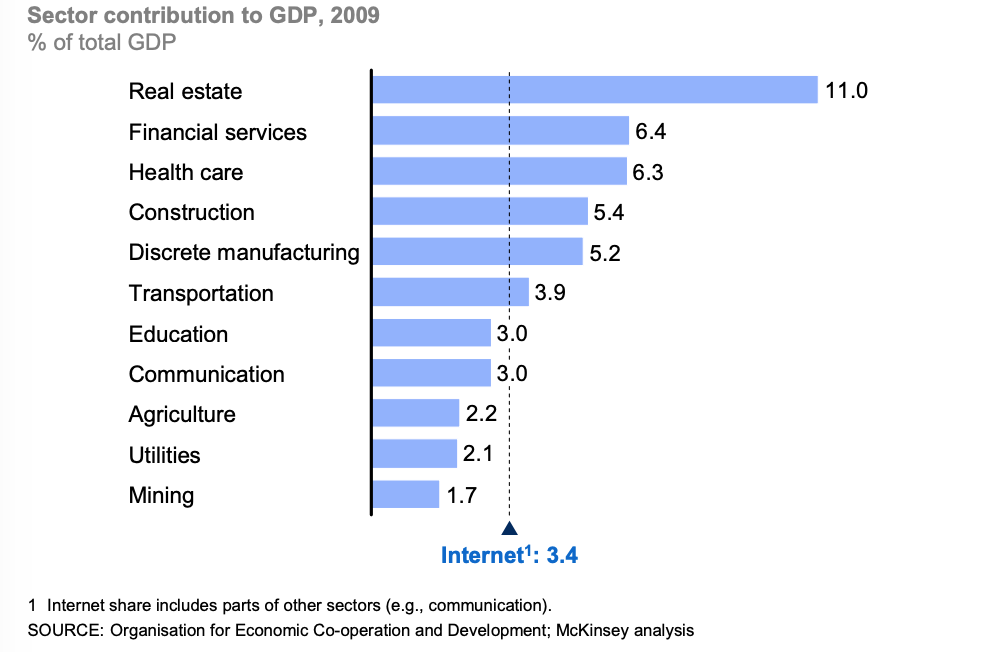
If measured as a sector of the GDP, internet related consumption and expenditures, would be larger than the agriculture and energy sectors. In the McKinsey Global Institute study on broadband internet and economic growth and prosperity, internet accounted for 3.4% of the GDP in the 13 nations researched.
Internet speed can be used as an economic indicator because it correlates with a given countries internet contribution of GDP. Countries with a strong internet supply in terms of speed and broadband connectivity strength correlate with a higher internet contribution to GDP. For example, Sweden and The United States have the best “internet ecosystems” in the world and this correlates with their internet contribution to GDP. Which is respectively 3.9% in Sweden and 4.7 % in the United States. The average internet connection speed in Sweden is 22.5 Mb/s and 18.7 Mb/s in the United States. When compared to Germany which has a lower average connection of 15.3 Mb/s, internet related expenditures only account for 1.9% of the Germany’s GDP.
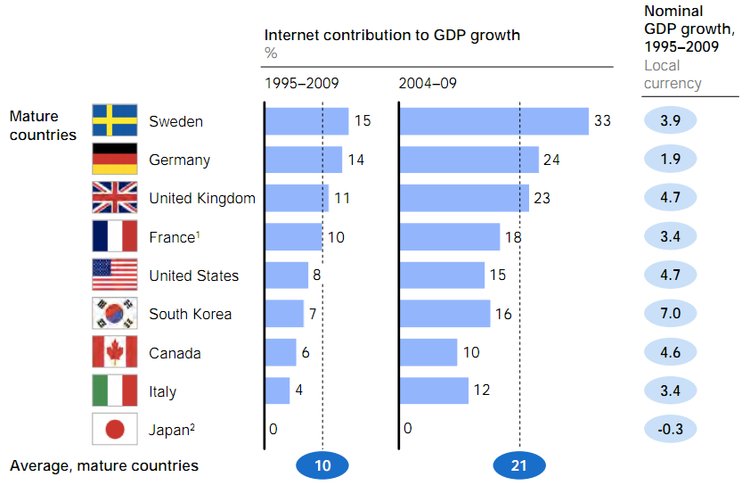
However, it is important to highlight that in most studies on developed nations it is noted that this positive correlation of broadband strength and economic growth reaches a threshold and other economic indicators should be used in conjunction when accessing economic growth.
Sources:
https://www.statista.com/topics/2237/internet-usage-in-the-united-states/
https://www.businessinsider.com/mckinsey-report-internet-economy-2011-5
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_countries_by_Internet_connection_speeds
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.