It is often said that the decisions of one impact the lives of many. Decisions on what to spend money on and when to spend accumulate into a collective force that dictates the growth or decay of the economy. This means that, behaviorally, the confidence the individual has in the continuation of their income will dictate whether or not they decide to spend money at that point in time in the first place.
Large investments such as cars and property have been used as a means of measuring the confidence of that consumers have on their economic future. Because of the size of the cost, money is often borrowed for such purchases and these goods are often used as equity for other loans. When the economy is doing well, people are more inclined to purchase homes and cars (both old and new) with the assurance that they will be able to pay off the debt of their mortgage or car loan. On the flip side, during a recession, sales tend to slow as consumers become more reluctant to make such risky purchases due to the chances of defaulting and high interest rates. Overall, consumers tend to withhold their spending in most markets when their confidence in the growth of the economy, and their spending money, is low.
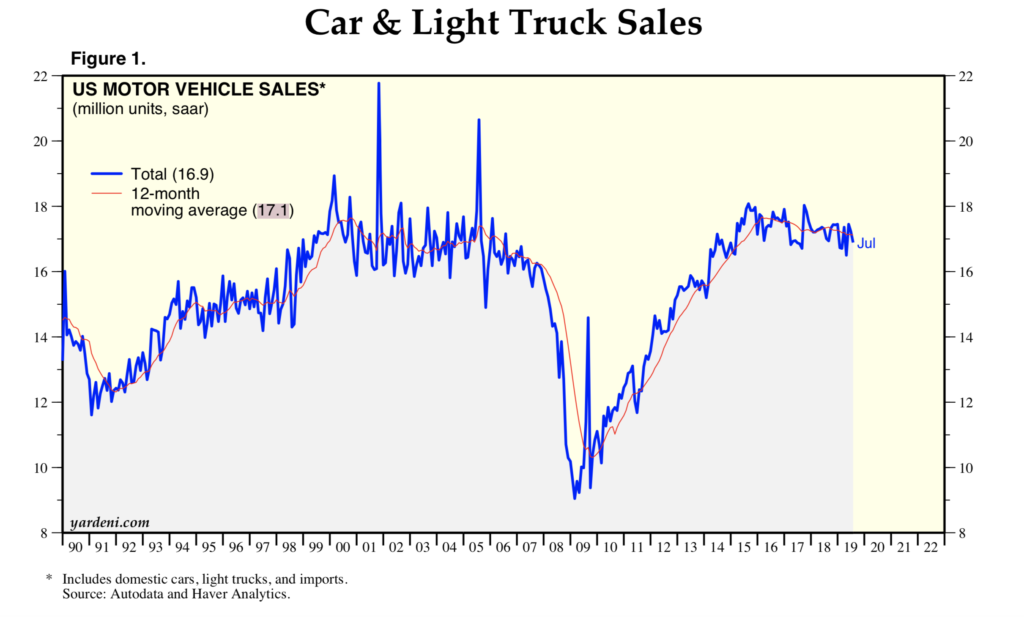
While it is often thought that all business tends to slow during a recession, there is one particular enterprise that actually benefits from an economic downturn: auto repair shops.
The heavy investment in vehicles makes commodities like cars precious. They endure regular wear and tear or collision damage, which inevitably leads to the end of the car’s use. Historically, car owners were more willing to trade their car in for a new model after every two years to avoid dealing with repair bills while enjoying the upgrades in fuel efficiency and better manufacturing.
During the Great Recession in 2007-2008, people divorced themselves from that habit to save money. As cars aged and began to break down, car owners had to invest in auto servicing, increasing auto repair sales by 10.5% from 2007 to 2011.
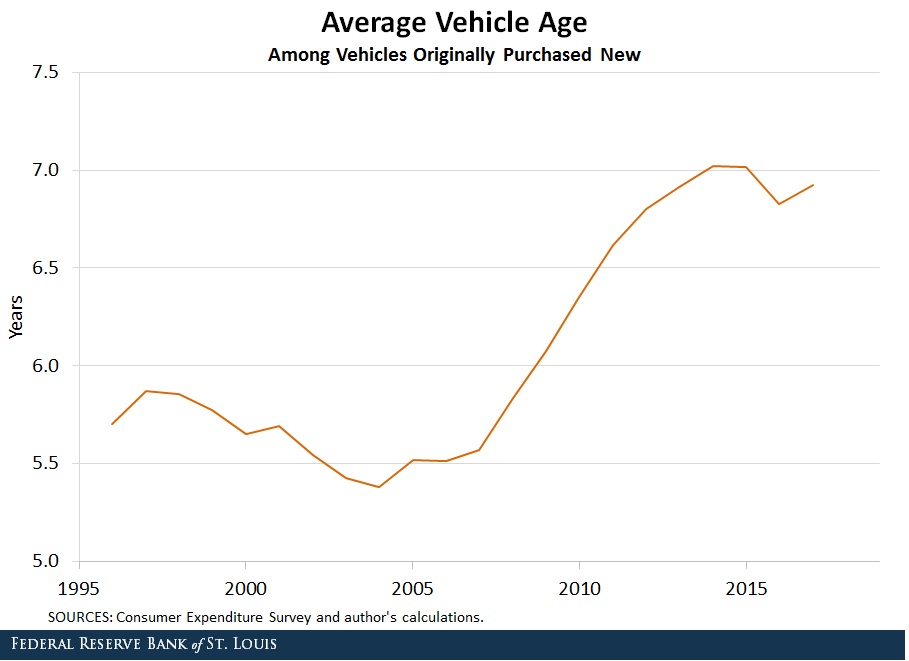
As with all indicators, there are a few factors to consider when analyzing the economy through auto repair sales. For one, it is important to note the rising cost of both cars and car parts due to new automotive technology such as self-driving and improved collision safety engineering, which can factor into the overall increase in consumer expenditure in that market. US-based insurers Travelers reports that the cost of repairing a 2018 sedan is up to three times higher than a 2017 model. These increased costs are projected to be an investment in driving safety, which could ultimately be offset by reduced frequency and intensity of vehicle accidents in the future, which means less-frequent spending on auto repairs.