
Although China has found major success in global hardware markets, they have yet left any major footprints in the digital space. Many anticipated that Chinese digital giants, such as Alibaba, Tencent, Baidu, and JD, would take over the tech world. Yet, their efforts have been disappointing and their results left many believing that China’s ability to crossover into the digital market would not occur. That is, until now.
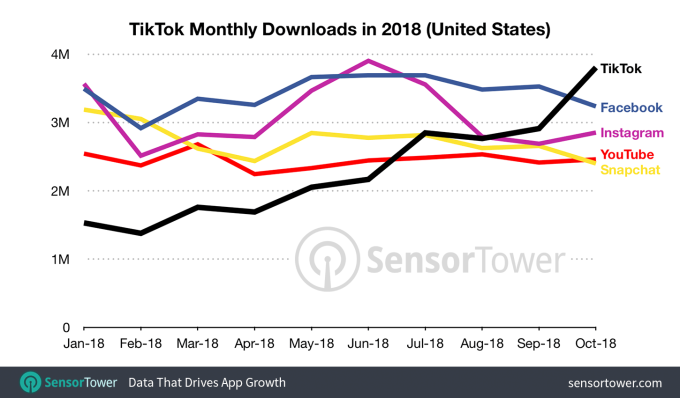
In 2018, the most downloaded apps in the U.S. included Facebook, Instagram, YouTube, Snapchat, and unknowingly for many, TikTok. TikTok became one of the most downloaded apps in the App Store for Apple users, and the Google Play Store for Android users.
What is TikTok?
TikTok is a video sharing platform that started with short music videos but has now expanded to include content that relates to cooking, travel, fashion, and so on. Videos on TikTok can be no longer than 15 seconds, but in those 15 seconds, content creators can add music and special effects through the use of the app’s simple tools. Because of TikTok’s easy-to-use functions, virtually anyone can become a content creator on TikTok. However, the most popular TikTok videos that have crossed over into Instagram and YouTube are high on entertainment value and set trends that many other creators on TikTok follow.
Although TikTok comes from China, it is not owned by one of the Chinese tech giants. Despite massive investments in video platforms, Chinese tech giants, such as Alibaba, Tencent, and Baidu, were never able to dominate this area of the digital realm. TikTok, known in China as Douyin, was launched in 2016 by ByteDance, a Beijing-based tech company traditionally focused on news. Its news app, Toutiao, uses advanced AI algorithms that learn user preferences, then provides customized news feeds. ByteDance uses the same algorithms to provide relevant video feeds to TikTok users.
By the start of 2017, Douyin had become China’s most popular mobile video app. In November of the same year, ByteDance spent $1 billion to acquire a competing video sharing site called Musical.ly. While Musical.ly was also founded in China, most of its users were based in the U.S. The combined global reach of TikTok and Musical.ly created a powerful combination that has generated China’s footprint in the digital market and a hopeful outlook on China’s digital future.

Competition Looms
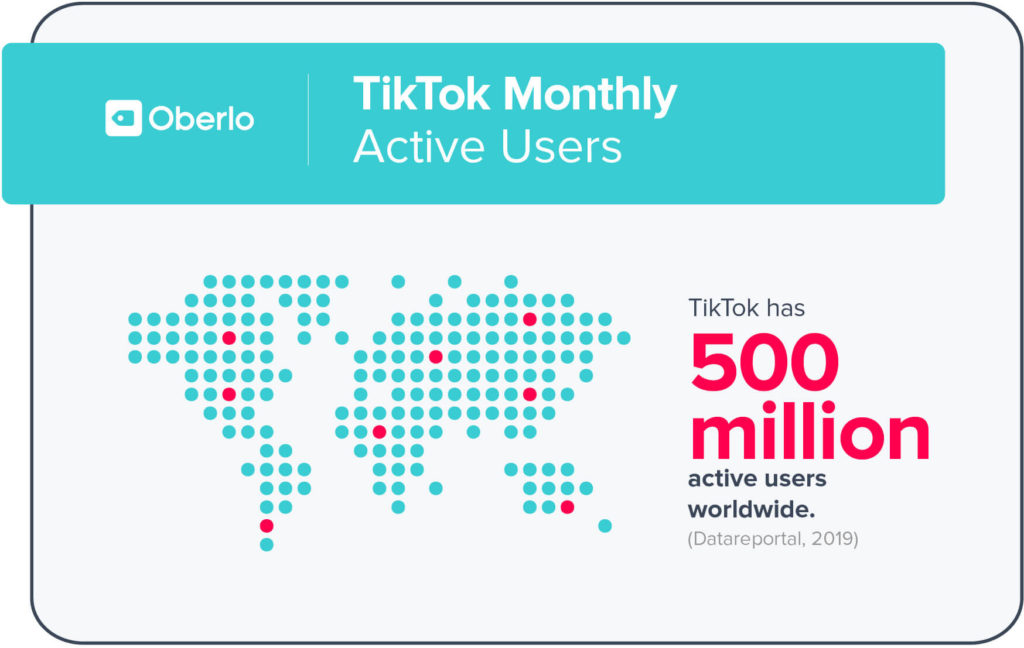
By the end of 2018, TikTok had more than half a billion active users, around 40% of them outside of China. Therefore, it is no surprise that Chinese tech giants have been closely studying TikTok’s successful approach of simple design, active promotion, and its utilization of trends in order to succeed in global markets.
Tencent is already trying to enter the short-video streaming industry by investing in Kuaishou, TikTok’s main local competitor, and reportedly giving out subsidies to promote its own platform Weishi. Those in the U.S. are also taking note, with Facebook quietly launching a TikTok competitor app called Lasso in November 2018.
Lasso has been downloaded by an estimated 70,000 U.S. users since launching in November 2018. This pales in comparison to TikTok’s 39.6 million U.S. users that downloaded the app in the same time frame. Although U.S. users make up a large portion of TikTok’s downloads, there is an undeniable presence TikTok has among the teens of the world with 500 million active users worldwide.
The Trajectory of TikTok
It is clear that TikTok’s growth is unheard of in the Chinese digital market and in the global space. However, ByteDance, the company behind TikTok, cannot become complacent with TikTok’s current place in the market, especially if it wants TikTok to build its position as the first globally successful “made in China” app.
The implications of TikTok’s success spans beyond materialistic accomplishments. It shows the global market that China has the ability to become major players in the digital realm, even without the backing of one of its tech giants. Therefore, combining large investments with TikTok’s successful strategic approach may lead to a “made in China” app market that competes with its global hardware markets.
Sources
- https://technode.com/2018/05/10/how-douyin-became-the-most-popular-app-in-the-world/
- https://www.reuters.com/article/us-bytedance-musically/chinas-bytedance-scrubs-musically-brand-in-favor-of-tiktok-idUSKBN1KN0BW
- https://venturebeat.com/2018/10/25/twitter-loses-9-million-monthly-active-users-in-q3-2018-its-steepest-decline-ever/
- https://uk.reuters.com/article/us-kuaishou-fundraising/chinas-kuaishou-in-1-billion-tencent-led-funding-round-eyes-ipo-sources-idUKKBN1FE11D
- https://kr-asia.com/tencent-bets-on-its-revived-weishi-app-to-take-on-toutiaos-tik-tok-in-short-video-streaming
- https://www.cnbc.com/2019/02/27/tiktok-is-staying-way-ahead-of-facebooks-lasso.html