On December 4th, 2014, Best Buy, the largest consumer electronics corporation in the US, announced officially that it would sell its Five Star business in China to the Jiayuan Group, a China-based real estate firm.

This was another huge movement for Best Buy in the Chinese market after it closed all its retail stores in China in 2011. After several years of struggle, the company finally decided to exit the Chinese market, only keeping some of the private label operations, with brand names that included Dynex, Insignia, Modal, Platinum and Rocketfish.
Although it seems to be the signal of Best Buy’s failure in China, investors are actually happy about that. The truth is, the company’s business in China didn’t bring any profit, but instead, it became a huge burden for the company on its way to further development.
The sale of Five Star business will bring about $300 millions to Best Buy, which allows the company to focus more on the North American business and further develop its online business section. Facing strong competition from online shopping websites like Amazon, the only way that Best Buy could survive is to transfer from a big box store franchise to a consumer electronic provider with different distribution channels, both online and offline.
Best Buy entered the Chinese market in the year of 2006 by acquiring local electronic franchise “Five Star.” Then, it opened nine mortar-and-brick stores in big cities like Shanghai and Beijing. At first, Best Buy applied the same business model it used in the US market to the Chinese market: the stores were located in city centers; the company operated it own inventory and bought products directly from other brands; the stores focused more on customer experience and after-sales service.
However, this kind of business model was not applicable to the Chinese market. Chinese customers are extremely sensitive with the price. However, as Best Buy insisted on managing its own inventory instead of lending space to other brands and letting them operate on their own, it was hard for Best Buy to lower its operating expense and provide a competitive price. While local electronic retailers, for example, Guomei and Suning, were able to provide consumers with a much lower price by lending space to other brands and saving huge operating expense, it was almost impossible for Best Buy to earn a favorable market share in China. Chinese consumers might go to Best Buy to experience the product, but when they actually made the purchase, they went to local electronic stores that offered a more competitive price.
The situation was the same in the US market. However, this time, Best Buy’s competitor was no longer mortar-and-brick stores, but the world’s e-commerce giant, Amazon. Unlike Best Buy, Amazon did not have to pay for the operating cost of real stores, and was thus able to provide a lower price. Also, the online environment for consumer electronic industry was already mature in the US. People felt comfortable with ordering electronic appliances online. As a result, Best Buy became a place where consumers could touch and experience the product, but it eventually failed to turn the store traffic into buying power.
Under this situation, Best Buy realized the need to make a transformation in its business model. However, as it was impossible for offline retailers like Best Buy to compete with Amazon on price, the company had to figure out another way to differentiate from its competitors.
As a result, in 2012, Best Buy’s new CEO Hubert Joly initiated a transformation project “Renew Blue,” aiming to combine the offline stores with online website and thus create an “ominichannel” that could make Best Buy products available to customers everywhere.
On one side, in order to save operating expense, Best Buy changed its business focus by closing big mortar-and-brick stores. In 2013 alone, the company shuttered 47 stores in the US, which saved it nearly $ 765 million in operating expense. At the same time, the company also opened more Best Buy Mobile stores, which were 10 times smaller than traditional stores. These small-sized mobile stores were located near the community, which made it easier for consumers to order online and pick up in the nearest store. At the end of 2012, the number of Best Buy Mobile stores had already reached 409, and was expected to increase continually in the future.
On the other side, Best Buy put more emphasis on developing its online business through “bestbuy.com.” Best Buy realized that the only thing that differentiated itself from Amazon was that the company had real stores where consumers could touch and feel the products. Hence, since 2013, Best Buy has been dedicating itself to connect its mortar-and-brick stores with the online website. Before that, Best Buy managed its offline store inventories and the online website separately. Some products might be available in the store, but didn’t show up in the official website. Now, as Best Buy successfully connected the two folds, people were able to shop across different channels, which not only brought more traffic to the offline big box stores, but also saved the company huge money on the shipping cost. In addition, it became easier for consumers to return if they were not satisfied with the product they ordered online after experiencing it in the store. In fact, Best Buy used its offline stores as a shipping center to support online sales, which provided better shopping experience to the consumers.
In addition, Best Buy also initiated store-in-store concepts inside the company. In 2011, Apple, Samsung, Microsoft and Sony reached an agreement with Best Buy to open their boutiques inside Best Buy stores, which saved money on both sides. By the end of 2014, Samsung has opened more than 1400 boutiques in Best Buy stores, which was almost the same number as Best Buy’s existing stores.
In the latest fiscal third quarter results, Best Buy reported a significant increase in its profit, which were two times the number of last year. In addition, the offline sales in the US also increased by 3.2%, which was relatively high comparing to other similar companies, for example, Wal-Mart.
Although the increase in sales doesn’t necessarily indicate the effectiveness of the transformation, it at least shows that the offline retail business is not dying. In fact, nowadays, e-commerce websites like Amazon have also realized the advantage of mortar-and-brick stores in their ability to provide better shopping experience to the customers. For those who want the product immediately, stores like Best Buy are still their favorable choice. As a result, in order to acquire that segment of customers, Amazon announced its first showroom in New York City while eBay put extreme emphasis on its “eBay Now” shipping service.

And as for Best Buy, its real stores seem to be the only opportunity for the company to differentiate from the other e-commerce websites. The combination of offline stores and online websites might be the only way to save companies like Best Buy in the future.

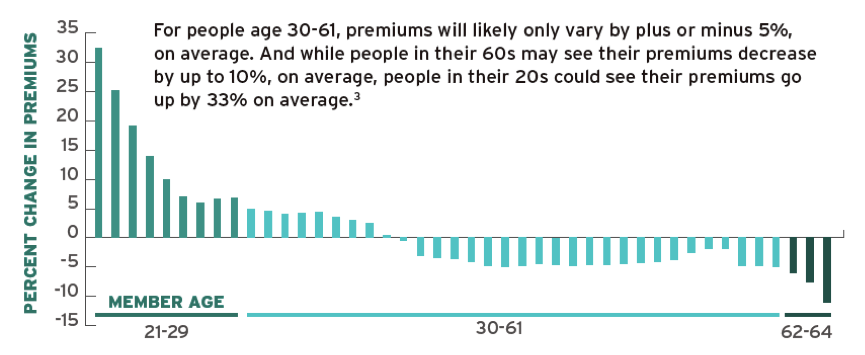
 Some people may argue that there are subsidies available for young people with limited income. Yes, there are. But the truth is, for those who earn a little more than the poverty line, it’s hard for them to choose whether to earn more with no subsidy or to earn less with a small amount of subsidy. More importantly, for those healthy people who usually don’t have health problem, they would rather end up with paying penalties instead of purchasing health insurance, which is far more expansive than the penalty.
Some people may argue that there are subsidies available for young people with limited income. Yes, there are. But the truth is, for those who earn a little more than the poverty line, it’s hard for them to choose whether to earn more with no subsidy or to earn less with a small amount of subsidy. More importantly, for those healthy people who usually don’t have health problem, they would rather end up with paying penalties instead of purchasing health insurance, which is far more expansive than the penalty.


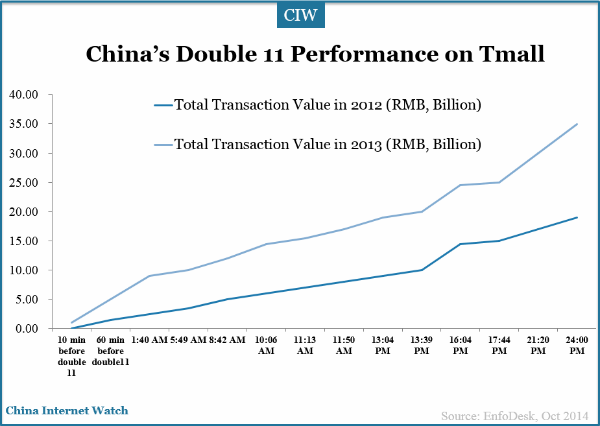
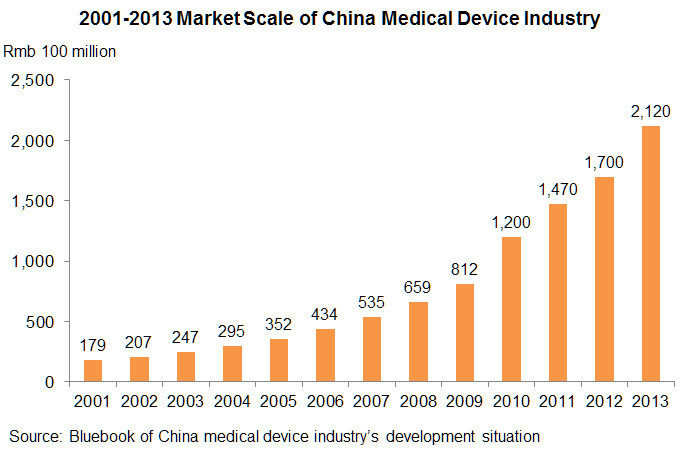
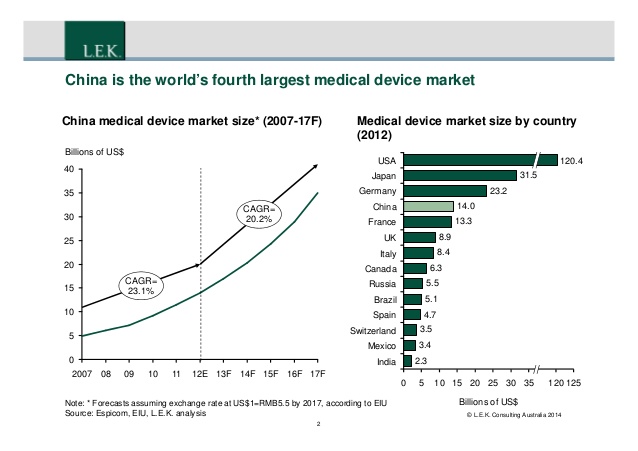

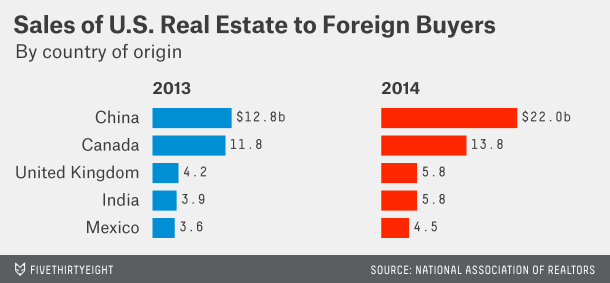
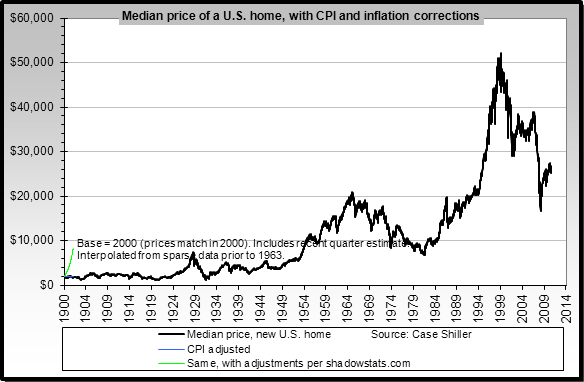
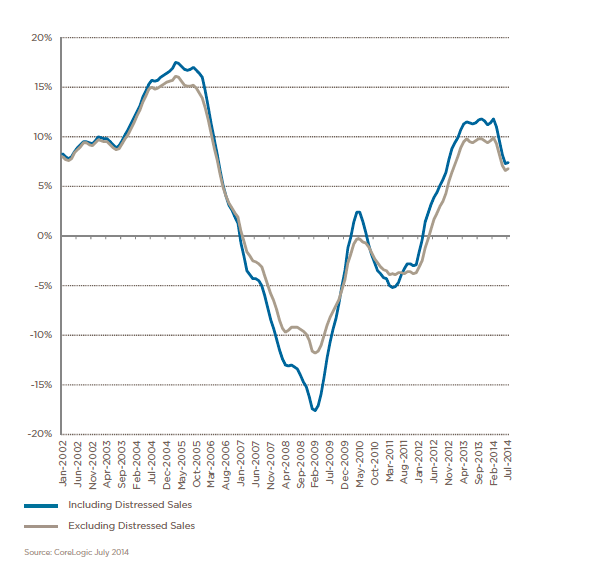 When asking about the future of real estate market in the U.S., Ji expressed her concern over the median-price house market: “One challenge we are facing now is that there are less and less affordable houses in the market.” While the demand for median price house is going up, the supply is actually going down. In July, the median transaction price was $457,000, which is 7.6% higher than that of last year. Also, the market volume, which is 7012 this year, is 12.5% less than that of last year, according to CoreLogic’s recent report. Ji is worried that if the interest rate starts going up next year, there will be more competitions in the median-price house market.
When asking about the future of real estate market in the U.S., Ji expressed her concern over the median-price house market: “One challenge we are facing now is that there are less and less affordable houses in the market.” While the demand for median price house is going up, the supply is actually going down. In July, the median transaction price was $457,000, which is 7.6% higher than that of last year. Also, the market volume, which is 7012 this year, is 12.5% less than that of last year, according to CoreLogic’s recent report. Ji is worried that if the interest rate starts going up next year, there will be more competitions in the median-price house market.