It’s easy to bemoan the capitalistic bend of the holidays: before the Thanksgiving turkey has settled in their bellies, many Americans are already stamping their feet in lines outside of Walmart and Target, ready to trample over their fellow man for a discounted plasma screen.
But there is a brand of capitalism designed to satiate the better angels of our nature: social entrepreneurship.
For an example of this, take Macy’s “Shop For A Better World” site, which is about as direct a mission statement — and a plea — as one can hope to find.

Fairwinds Trading, a social enterprise that funds artisans in developing countries, partners with Macy’s to supply consumers with “gifts that give hope.”
Browsing the site, you’ll find “Heart of Haiti All-Horn Salad Servers” (for $42), or “Rwanda 10th Anniversary” woven baskets ($50-$60). This may seem pricey, even for “culturally expressive” gifts, but consider that the artisans (that is, the Rwandans and Haitians making these salad servers and baskets) receive half of the wholesale price and suddenly, that price doesn’t seem so outlandish. In fact, spending that extra $20-$30 could leave you feeling pretty darn good.
And here you have the draw of social entrepreneurship. Because if you or your loved ones are going to be serving salad anyway, why not make sure you’re making the world a better place doing it?
The appeal of social entrepreneurship is that it blends traditional capitalism with solutions to societal problems big and small, like providing water to drought-stricken areas of the world or funding SMEs in Haiti. Through social entrepreneurship, start-ups blend business with creativity and create “shared value” — that is, not just economic value, but value to society.
But as widespread as the practice has become, social entrepreneurship lacks a clear definition. Wikipedia (which itself could be considered a social enterprise) defines it as “the attempt to draw upon business techniques to find solutions to social problems.” So, Kiva, which provides micro-loans to small business owners in developing nations, is a social enterprise, as is Fair Winds Trading, the company that supplies Macy’s with its Rwandan woven baskets, and (according to ashoka.com), Susan B. Anthony is a prime example of a social entrepreneur.
Wait, huh?
If that last example caused you to furrow your brow, you’re not alone. And that may be one of the problems confronting social entrepreneurship: if you can’t really define it, how do you know a good (or poor) example of it? How do you know if it’s working?
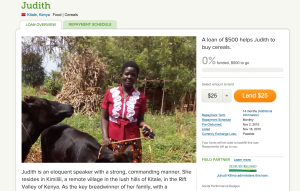
One way to look at it is that the consumer isn’t just purchasing a solution, but a story. For example, when you provide a $25 micro-loan with Kiva, not only do you get to personally select your borrower (each borrower is screened by Kiva and has a biography on their site), you get regular updates on how their business is going. It’s not just the appeal of lending money to a needy or deserving, but anonymous, business owner that draws people to Kiva, it’s that you get to ensure Judith from Kenya’s success by helping her buy cereals to sell at the market.
But not only can a good story convince a consumer to open up her wallet, in the case of Sejin Kaleb Oh, founder of Gravity LA, having what he calls a “higher purpose” can keep a business owner motivated.
Gravity LA is a pretty traditional clothing retailer, selling a handful of tees, pullovers, and tanks that are “reputable” and “sweat-shop free,” according to their site.
But click on their “about us” section of their page and you’ll find the following:
“GRAVITY LA was founded on December 21, 2013 to raise money to support those that are willing to leave their comfortable homes and venture out into the unknown and dangerous to bring hope, life, and love to those that are desperately in need of it.”
How do they do this?
According to Oh, they take a percentage of whatever profit they make and donate it to charity.
That’s pretty much it.
And as close as his charitable donations are to his heart, Oh doesn’t set a percentage, so he doesn’t advertise one, and even he says the purpose of the shop isn’t exclusively to raise funds for charity. But what these donations do give him is a cause to answer to when the going gets tough — as it often does for entrepreneurs.
“It’s the story of why I exist, or it’s the story of why Gravity LA exists,” said Oh.
“If you’re just out there for money,” Oh said, “you’re in the wrong business. Because you don’t really see any return on it for years. It’s really that purpose that keeps you going. And really, I don’t know how companies do exist without a story like that or without kind of purpose driving them. I think it’s vital for the life of any business.”
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.