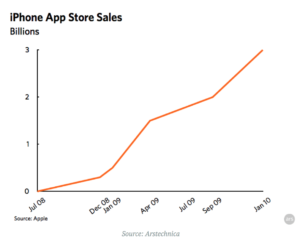
In 2016 consumers spent around $30 billion on video games. Historically, video game consumers spent that money on a single game that unlocked all of its features. However, more recently, video game developers are distributing free-to-play games on the App Store, the internet, Steam, etc. in exchange for introducing microtransactions.
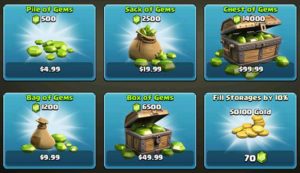
Microtransactions are transactions within a game that allow players to unlock virtual items that help them progress in a game or make their character look better with weapon skins.
With the advent of the App Store, small game developers saw this as an opportunity to sell their games for free but work in transactions so that players could add to the game. Clash of Clans, despite being a free game on the App Store, made $2.3 billion dollars last year. Microtransactions go beyond the App Store, too. League of Legends, a free game made by Riot Games, made $1.6 billion in 2015 off of Microtransactions.
Microtransactions are leeching into full-price video games as well. The new game, Star Wars Battlefront II, was released with a lot of controversy. The $60 dollar game (the deluxe edition costs $80) was going to be released with a microtransaction system. To get loot crates, which can unlock heroes like Darth Vader and Luke Skywalker, and help a player progress through a game, people would have to pay up. Electronic Arts removed that system before the game came out, after public outcry by gamers and a post which earned EA the highest number of downvotes ever on Reddit.
For big box games like Battlefront, the idea is to create a continual revenue stream for a game even if its initial price depreciates. Within a year some games can lose more than half of their value as new games come out and replace the old ones, similar to cars, though at a much faster rate.
Microtransactions employ behavioral economics. There are a whole slew of tactics, but there are two main ideas that trick people. First, they have weird conversion rates from dollars to an in-game currency, so it is hard for players to know how much money they have spent. Second, developers treat microtransactions like gambling. Players can put in money to get that in-game currency in the hopes that when they unlock a loot box they will get a great prize.
Microtransactions are likely going to be around for a while, and as artificial intelligence takes off, they will probably become more specified to a person’s play style, the friends they have online and a whole host of other variables. Gamers have at least staved off microtransactions in Battlefront, for now.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.