Li Ka Shing, Hong Kong’s wealthiest man started his career as a high school drop out but he managed to grow his wealth alongside Hong Kong’s rapid financial boom. Anything good that has happened to him could be traced back to the fact that he was born in the right country, Hong Kong, at the right time, 1930s. He was not the only one to benefit from his birth, Warren Buffet, probably the world’s most successful investor was born around the same time in the United States. A quarter of a century ago, when The World in 1988 ranked 50 countries according to where would be the best place to be born in 1988, America indeed come top. But the question is, which country will be the best birthplace for the years to come?
To answer this, The economist has created a comparison of 80 countries which will provide the best opportunity for healthy, safe and prosperous in years ahead. The quality of life index (also known as the where-to-be-born index) links the results of subjective life satisfaction surveys – how happy people say they are- to objective determinants of the quality of life across countries. A high GDP per capita helps more than anything else however it is not all that counts. Things like crime and trust in government institution matter too. Overall, the index takes 11 indices into account, they are varied but all important considerations: some are factors hardly ever change (geography), and others change very slowly (social and cultural characteristics) and some factors depend on political environment and the state of the world economy.
Determinants of the Quality of Life
1. Material wellbeing
- GDP per person, at ppp in $.
2. Health
- Life expectancy at birth, years.
3. Political stability and security
- Political stability and security ratings.
4. Family life
- Divorce rate (per 1,000 population), converted into index of 1 (lowest divorce rates) to 5 (highest).
5. Community life
- Dummy variable taking value 1 if country has either high rate of church attendance or trade-union membership; zero otherwise.
6. Climate and geography
- Latitude, to distinguish between warmer and colder climes.
7. Job security
- Unemployment rate %.
8. Political freedom
- Average of indices of political and civil liberties. Scale of 1 (completely free) to 7 (unfree).
9. Gender equality
- Ratio of average male and female earnings, latest available data.
10. Governance
- Ratings for corruption
Surprising factors that weren’t included in the index are education levels, rate of GDP growth and income inequality. According to studies, education only had a small correlation to overall life satisfaction however, education levels can also impact political freedom, job security and gender equality.
A forward-looking element comes into play too. Although many of the determinants of the quality of life change rather slowly, these rankings are only a forecast. The2013 index will be for children born in that year and predict the year 2030 when they reach adulthood.
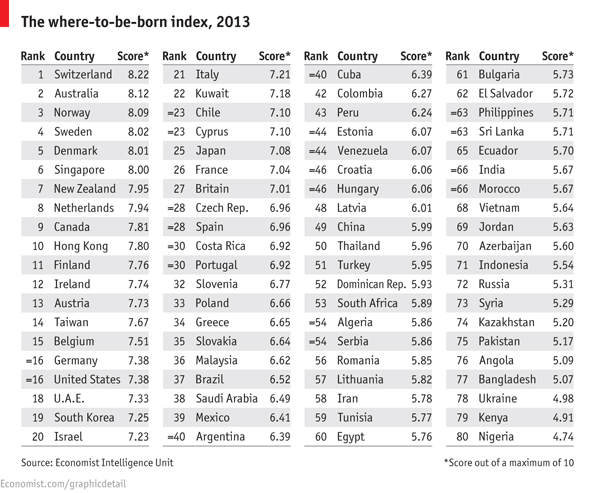
Small economies dominate the top ten places. Half of these countries are european but only one country is in the Euro Zone (Netherlands). The Nordic countries are ranked the highest whereas European economies with high unemployment rates lag behind (Greece and Spain) despite their advantage of a warm climate.
America, the number 1 country to be born in in 1988, is down in 16th place, despite their huge economy and political freedom, babies born today will inherit large debts of the boomer generation. None of the large manufacturing countries such as Brazil, India or China scored very impressively.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.