Online food ordering and delivery service is a highly competitive industry in Los Angeles. Some startups, however, smartly take advantage of their upper hand and successfully get into the market left untouched by many bigger players like GrubHub and Eat24.
Kirin Kang emigrated from China to U.S. six years ago. Until 2013, He worked as a sales man in a trading company. In his one-hour lunch break, Kang usually spent 40 minutes on ordering and waiting for his lunch, and then the rest 20 minutes on quickly swallowing the food. Kang later found his friends, colleagues, and other working class people have the same issue.
“How I wished to have a 10-minute break after my lunch,” Kang said, “ So I though if I can order food online and someone can delivery it for me, then my life would be much easier.”
In 2014, he decided to be person who provides the convenience. Since arrival, Kang has been living in the San Gabriel Valley, where the telephone area code is 626, so he named his company as ToGo626.
“I live in the 626 area and it’s also my major market now” said Kang, “I want to do something good: bringing Chinese food beyond this area.”
ToGo626 has partnered with over 90 businesses within 2 months. Most of them are Chinese restaurants.
“Speaking Mandarin helps me a lot in this process,” Kang said. “I communicate with the businesses owners in Mandarin and translate their menus from Chinese to English.”
As most of his customers are Chinese people, Kang had both Chinese and English version of ToGo626.com.
In April 2014, the biggest online food ordering and delivery site, GrubHub, initiated public offering at the price of $26 per share. It raised $200 millions in total. As the CNN Money reporting says, the company estimated to worth $2.7 billion at the current price. On the website, there are 3564 restaurants in Los Angeles partner with GrubHub.
Valley Boulevard in San Gabriel Valley harbors many popular Chinese restaurants like Boiling Point, Shanghai No.1 Seafood and Szechuan Impression. But these restaurants on can barely be found on GrubHub.
Eat24, as another big player in this industry, provides a few more Chinese food options, but still, many popular Chinese restaurants are off its list.
“Language barrier might be the reason why they haven’t opened the Chinese restaurant market for so long,” Kang analyzed.
Another startup called RushOrder shares the same notion. Like ToGo626, RushOrder focus on the Koreatown area.
“A lot of our team members, including myself, were raised in Koreatown. I still live there,” said Henry Choi, leading the sales and marketing department of RushOrder. “So we have this advantage than the bigger players in the industry — we know the area, the language, and the popular restaurants.”
With the help of the mother tongue, Korean, Choi and his team members were able to bring in 55 Korean restaurants within 3 months.
“Overall we are planning to go live with about 300 restaurants in the next a couple of months,” Choi said. “One of our goal is to provide Korean cuisine to people that may not have necessarily known about it. So if they go to the restaurant and see the menu, they might be intimidated and they don’t even understand what it is. So what we can do is we can fully translated and explain to them.”
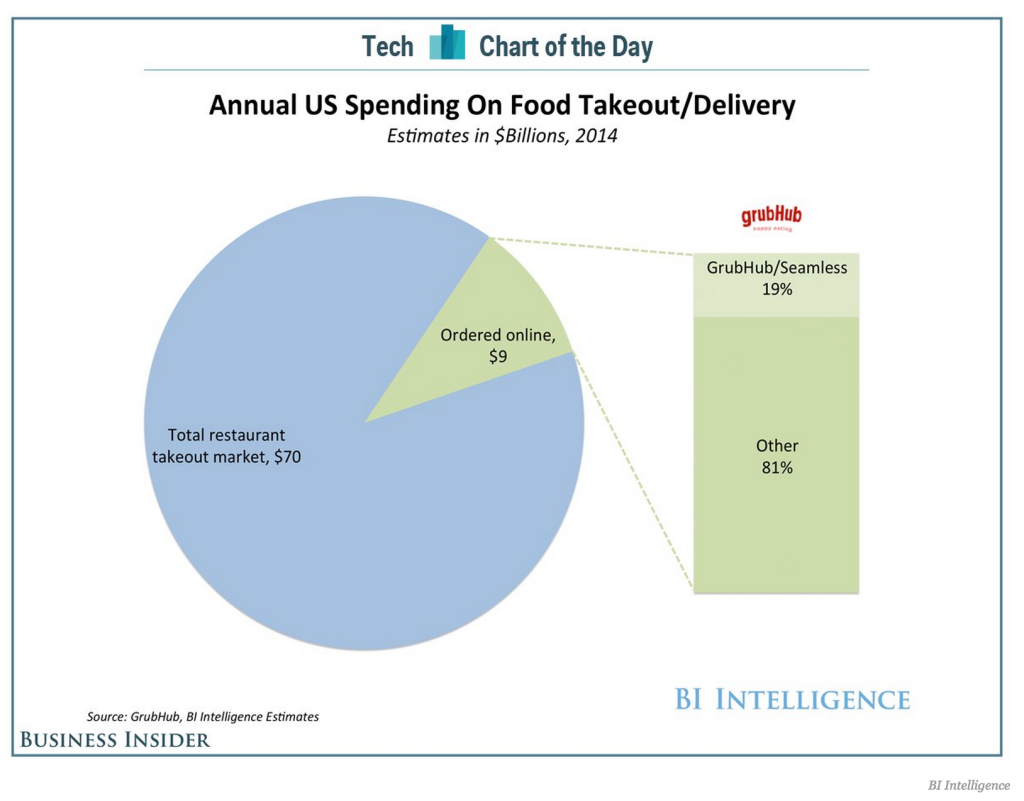
Americans are estimated to spend $70 billion on food takeout and delivery in 2014, according to BI Intelligence. $9 billion out of that amount will be spent on online orders. Grub and Seamless merged in August 2013, and they will altogether take up 19% of the share. The rest 81% is divided by different smaller service providers.
Uber, the ride sharing company, is also trying to get a slice of the cake. Since August, 2014, it has been testing a food delivery service called UberFRESH. Currently, the service cover two areas: Westside and Beverly Hills/West Hollywood. The ordering time for lunch is between 11:00 a.m. to 1:30 p.m.; for dinner is 5:30 p.m. to 8:00 p.m.
UberFRESH claims the meals can be delivered within 10 minutes, compared to 45minuts to 1 hour of other similar services. And the delivery fee starts from $3 no matter how many meals the customer order.
Just like requesting the Uber ride, customers can order food delivery service online.
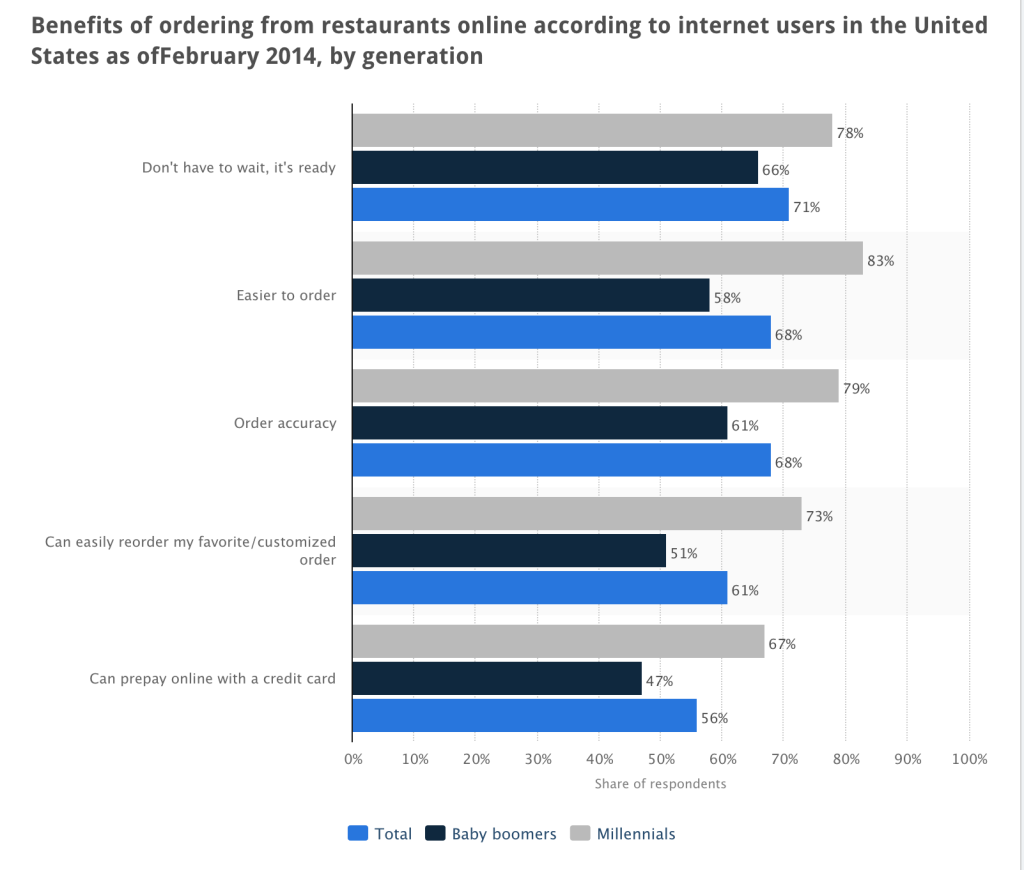
EatStreet is also an online food ordering and delivery service provider. Marcus Higgins, VP of sales, told QSRweb.com “The reason consumers prefer online versus traditional (phone or in-person) orders is because it offers instant gratification. It’s all about being able to have the convenience to go online, look at a menu, look at the items you want and not have to wait for someone,” he continued “There are also other benefits, such as order accuracy and price checking, the elimination of any language barriers, and the convenience of already having your payment information on file, instead of having to enter it every time.”
Higgin’s analysis echoes with the survey done by Statista.
The convenience brings ToGo626 around 100 orders during weekdays. “There may be more on weekends,” Kang said.
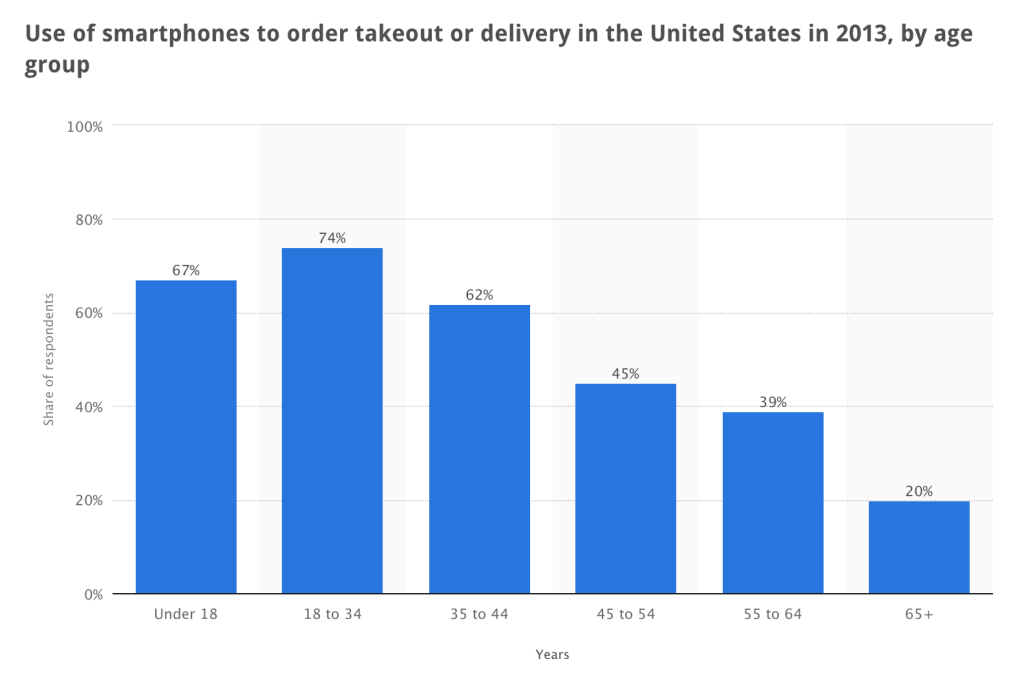
Thanks to the spread of Internet and smartphone, the age of customers using online ordering and delivery service is getting younger and younger. Most of the customers’ ages are between 18 to 45 for both ToGo626 and RushOrder.
“There are students, working class people, and parents that order food for their kids at home,” Kang said.
The online food ordering and delivery service not only benefits customers, but also helps bring more orders to businesses, and the service providers, in return, generates revenue from that.
“The way our business works is that the restaurant pays us depending on how many orders we bring to them,” said Choi from RushORder. For every months, “0-25 orders, is free. 26-100 orders, is 50 dollars. Anything over 100 orders is 100 dollars”
“We actually use a delivery company. The cost that the delivery company charging us, is what the customers paying for,” Choi continued. Therefore, the major revenue of RushOrder comes from businesses rather than customers.
Unlike RushOrder, ToGo626 has a 15-driver delivery team and some volunteer drivers. “But our delivery fee is only about $0.99 per mile,” said Kang, “So delivery is actually a supplementary service.”
Kang treats ToGo626 more as a platform to promote and advertise restaurants. Most of the restaurants provide sponsorship to keep the partnership with ToGo626.
However, not every business owner is aware of the influence of the Internet. Some of them are middle aged or even seniors. The big age gap made it hard for Kang to persuade them into joining the adventure.
When communicating with some traditional Korean restaurants, where orders are written on a piece of paper and orders can only be paid by cash, Choi encountered the same problem.
Accumulated popularity and fan base help solve the problem. Not only fans help recommend businesses to ToGo626, restaurants are also reaching out to Kang to get their name on the website.
As Kang promised, ToGo626 is helping restaurants with the online ordering and delivery service, as if they have branches in different cities.
RushOrder is trying to bring in more Korean restaurants. As Choi explained, one of their goals “is to provide access to non-Korean speaking people in Koreatown. Introductin them to the food, making it convenient for them…so they can try it out.”
Kang expressed the same feeling for ToGo626.
“This is only a start. A good start, maybe,” he said, “We will start from the 626 code area. After fully developing the market here, we will explore further, providing more choices, more restaurants and more cuisines to our customers.”