In an age where streaming movies on Netflix or Hulu has become the norm, many people assume the movie theater industry is a dying relic of a more financially stable time.
In an age where streaming movies on Netflix or Hulu has become the norm, many people assume the movie theater industry is a dying relic of a more financially stable time.
Every year, Hollywood releases reports blaming mediocre films for turning audiences away. Other people in the media think the industry is failing because younger generations are less interested in the big screen experience. Unfortunately, most of these reasons lack any statistical support.
The movie theater industry follows a rollercoaster-like business cycle that reaches its peak during different periods of time much like many sections of the U.S. economy. However, the unique characteristic of the movie theater business is that it thrives when most businesses are struggling to survive.
This is the Buttered Popcorn Index.
Throughout the history of U.S. cinema, there has been a trend in movie theater attendance as it correlates with the economic climate in the country.
During the Great Depression, the film industry had to cut costs in production and theaters had to lower ticket prices. This led to an enormous surge in the film industry with roughly 60 to 80 million people heading to the movies each week.
In 1982, movie theater attendance climbed 10 percent while the unemployment rate increased at a similar pace. However, as the economy healed, attendance dropped about 12 percent.
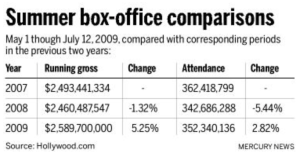
Now let’s look at our most recent recession. In 2008, the movie theaters earned roughly thirty million dollars less than in 2007. In 2009, the summer box office had an enormous spike in ticket sales after declining in 2008. The chart above shows how, between 2008 and 2009, theaters earned over one hundred million dollars more than 2008.
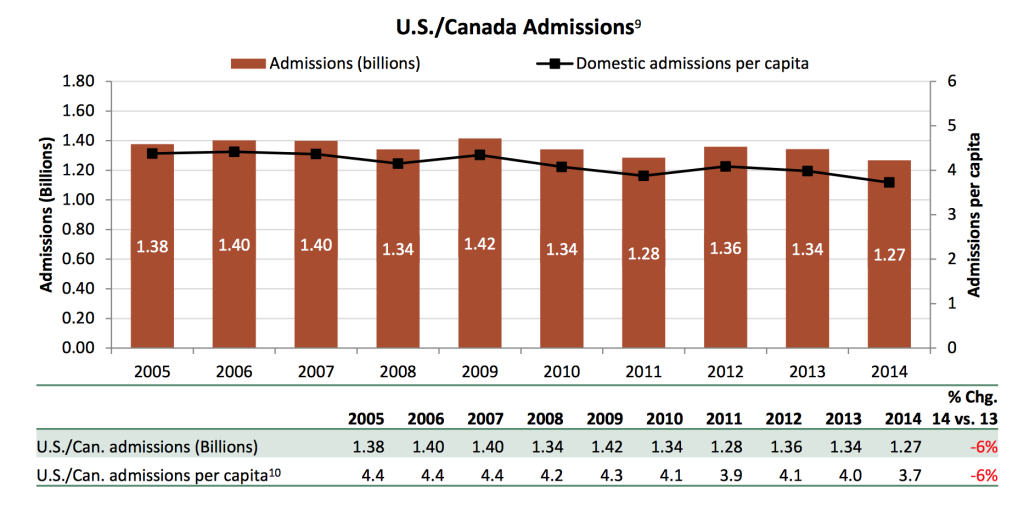
Movie theaters have not been able to maintain the 1.42 billion people they brought in during the rescission. The Hollywood Reporter released statistics in 2014 stating the number of people going to the movies had dropped six percent from 2013, which was the lowest in twenty years.
Ticket prices have played a large role in how people perceive the movie theater experience. Between 2001 and 2015, The price for move tickets increased from $5.66 to $8.12. The prices have blown up dramatically within the last fifteen years, yet there were more people going to the theater in 2009.
One of the main reasons why movie theaters had a surge during the recession was because even with the rise in prices, tickets have remained below ten dollars. Therefore, when times are tough for people, less of them look at going to the movies as an expense and more as one of the few remaining affordable options for entertainment.
“Generally, when economic downturns hit, we have seen an increase in box office and attendance in six of the eight last recessions,” said spokesman for the National Association of Theater Owners Patrick Corcoran in an interview in 2011, “People seek relief in forgetting their problems, so they go to the movies, and it is the least expensive form of entertainment.”
Another reason for the success of the movie theater business in 2009 was the types of movies being released. Happier films like Pixar’s Up and the comedy film The Hangover raked in close to $300 million each during the summer months. This suggests many people were looking for an inexpensive way to enjoy themselves in a tough economic climate.
The Buttered Popcorn Index demonstrates that no matter what era it is, people tend to flock to movies to escape the realities of their financial situation.