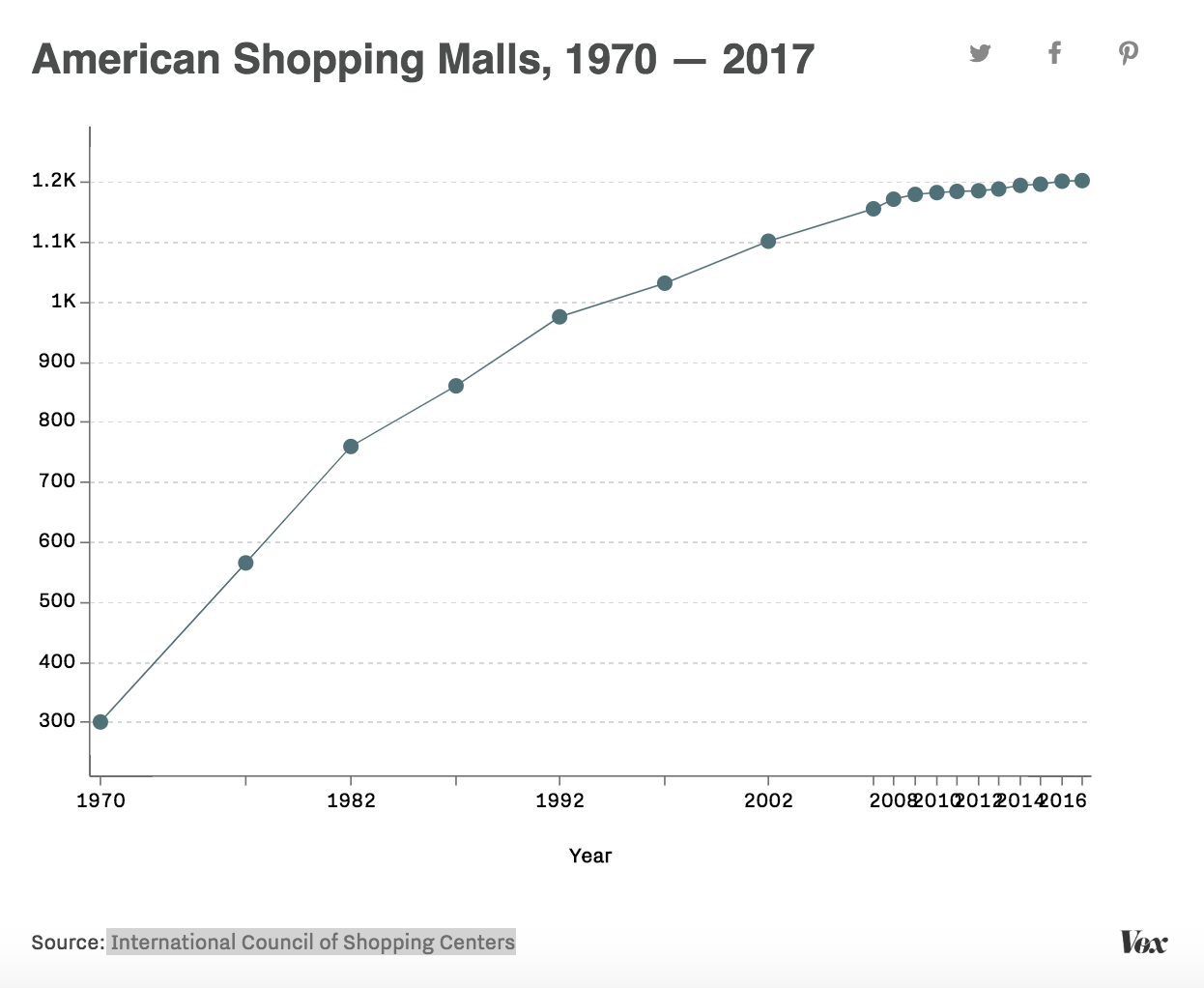
If you want to find an example of the current state of American shopping mall, you may want to take a visit to Westside Pavillion in Los Angeles. Like so many dying malls across the US, Westside Pavillion is an eerie, empty site during operating hours. In better days, the mall was the site for movie shoots and music videos. Now, anchor stores like Nordstrom and Macy’s have left the mall, leaving only the Landmark Theatre, Urban Home, and Macy’s Furniture Gallery behind. The mall is set to close in 2021, and will be remodeled for office space for media and tech companies. Westside Pavillion’s story isn’t unique. For instance, a quarter of American malls are in danger of closing.
However, some other shopping malls tell a different story. If you take the twenty minute drive to The Grove, you’ll find a different sort of retail story. Customers flock towards it’s luxury department stores and stroll through a nostalgic boulevard with a matching emerald green trolly. Built in 2001, as a “Main Street for a city that does not have one” some may see the Grove as a shining example of the new american mall. You can find the same open air, luxury stores, and experiential designs in other popular, revamped malls like Westfield Century City and Santa Monica Place.
So why are some malls doing better than others? While many American malls are closing, the survivors are adapting in order to accommodate the new offline retail experience: luxury goods and attractions. As online retail continues to grow, dying malls and retail also affect labor demands and deplete a form of revenue for some vulnerable counties.
Symptoms
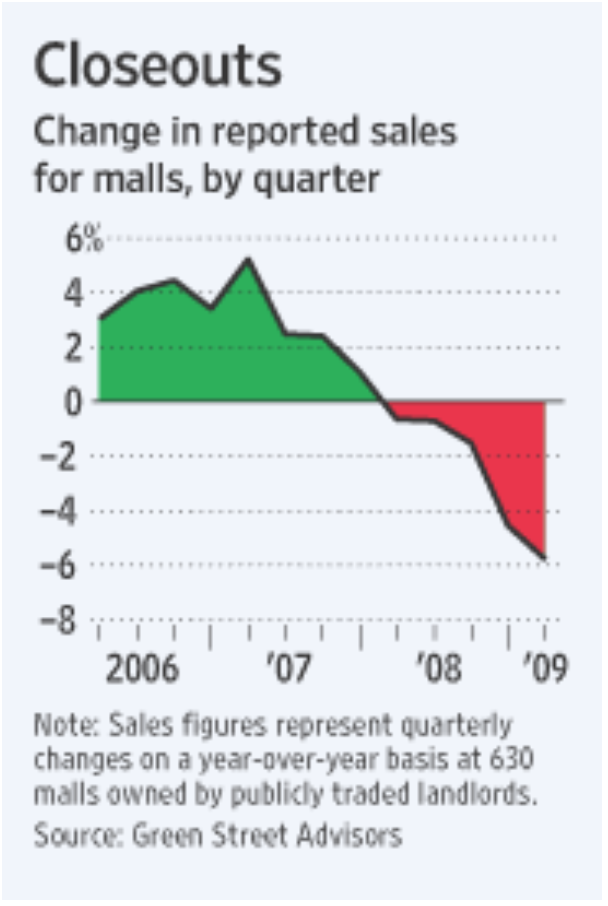
How does a mall begin to die? Data shows that one symptom was the Great Recession. plowing While the recession helped put brick-and-mortars like Toys ‘R’ Us, Sports Authority, and Circuit City out of business, it had a lasting effect on malls as well. General Growth Properties, which owned almost 18 percent of American malls during the recession, filed for bankruptcy in 2009. A lack of customer traffic drove profits down. It was difficult to turn dying malls into repurposed spaces due to declining property values and the subsequent end of the building boom. Online retail also aided in the decline of American malls following the Recession. While internet retailers represent just about 10 percent of retail sales, mall stores like Claire’s, Radioshack, and Pacsun struggled to compete with online demands.
As both department stores and small tenants began to close, vacancy rates began to rise. In 2008, the total vacancy rate for US shopping malls was 7.1 percent, compared with 5.8 percent in 2007. However, there is some evidence that the mall development explosion in the 80s and 90s just created too many stores to survive through economic recession. For example, almost 60 percent of Macy’s closing stores today are within 10 miles of another Macy’s location.
In contrast, Nordstrom, a department store with higher price-points, has adapting changes in online retail. In addition to opening more locations, Nordstrom generates almost a quarter of its sales online, that rate is higher than its competitors in Macy’s, Kohls, and Jacey Penney who hover around 15 percent. Even with the rise of e-commerce, sash-strapped middle and working class customers have found other avenues to find what they need for lower prices. Ulta Beauty, TJ Maxx, and the Home Depot have moved into fill the needs that these anchors used to fill and continue to open stores.
When anchors close, the smaller tenants close up shop, leading to more dying malls. As of October 2018, closings of anchors like Sears, Bon-Ton, and JC Penney and mall stores like J. Crew, Abercrombie & Fitch,have pushed the total enclosed mall vacancy rate to 9.1%. However, while B, C and D class malls- or malls in “in less desirable locations and home to less coveted tenants with lower sales per square foot” are vulnerable to vacancy rates and closing, the luxury mall or A class, has shown signs of success.
Only the Strong (or Wealthy) Survive
“Within 10 to 15 years the typical U.S. mall, unless completely reinvented, will be seen as a historical anachronism, “said Grove developer Rick Caruso at a National Retail Federation’s annual convention in 2014.
The “typical U.S. mall” had a Macy’s, Boscovs or Dillards. It had parking lots, skylight, and a food court. It catered towards a growing middle class with cash to spend with stores that fit their income bracket. But, Class A malls, or the kind of retail experience that Rick Caruso has built with the Grove: luxury department stores, expensive brands, and fine dining with a walkable “main street.”
While other Class A malls may lack the Caruso’s visual flare, the bare bones of their business plan is similar. The King of Prussia mall, the second largest mall in the US, underwent a 155,000-square-foot expansion and ushered in luxury tenants like Cartier and Jimmy Choo. While luxury department stores like Neiman Marcus, Saks Fifth Avenue, and Nordstrom have fewer stores, they have locations in the majority of the the nation’s most successful malls.
According to research by Boenning & Scattergood, the 20 most valuable malls in the country make more than 21 billion in retail sales. According to Fung Global Retail & Technology, just a fifth of the nation’s luxury malls generate more than 75 percent of mall revenues.
At the same time, income disparities continue to widen in the US. According to Vox, in the years between 1980 and 2018, “the poorest half of the US population has seen its share of income steadily decline, and the top 1 percent have grabbed more.”
“It is very much a haves and have-nots situation,” said D. J. Busch, a senior analyst to the New York Times. Wealthier americans “will keep going to Short Hills Mall in New Jersey or other properties aimed at the top 5 or 10 percent of consumers. But there’s been very little income growth in the belly of the economy.”
Data also shows that millenials have less money than previous generations, as stagnant wages, debt, and rising housing prices cause millenials to spend “nearly $20 less every day than their counterparts roughly 10 years ago,” according to a recent Gallup poll. And as almost three quarters of millenials prefer to spend more on experiences than material items, the malls have to adapt to that need with expensive renovations.
As anchor stores marketed towards working-to-middle-class clientele close and brick-and-mortar retail demands change, luxury malls remain. If all the business has flowed towards malls with the ability to finance opulence and entertainment, what happens to the communities that called those now dead malls home?
A Post-Apocalyptic Future
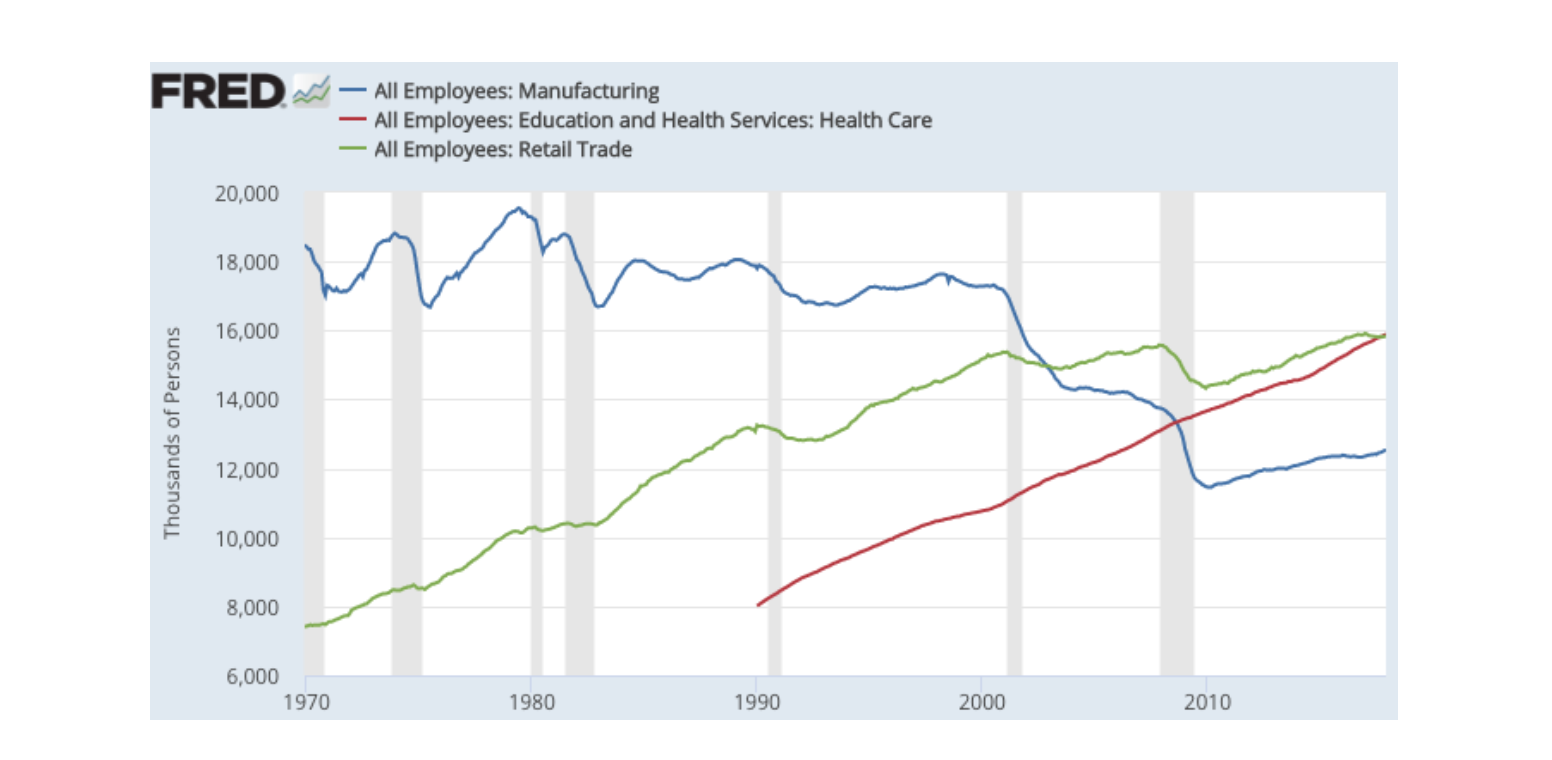
As customers lose their shopping malls, local workers lose their jobs. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, Department stores have shed 500,00 jobs since 2002, which is almost is almost 18 times more workers than coal mining.
Before the Recession, 2.4 million workers were staffed in retail than manufacturing and health care. However, ten years later, the education and health services industry employs more than 34.48 Americans, while the retail industry employs 20.3 million.
The rise of e-commerce industry has also opened up job operuntities. Amazon and other companies continue to higher more and more workers to staff fufillment positions in warehouses, all the while holding competitions to develop even more effecient robots to work in those warehouses.
Even as American workers adapt to changing demands, communities will have to adjust from the revenue benefits of brick-and-mortar retail. Montgomery County,PA gets 50 percent of its revenue from the King of Prussia mall, the 2nd largest mall in the US. However, the county is the second wealthiest in the state by income with around a $40,076 per capita income.Other counties across the mid-atlantic region stand to be affected by the loss of the revenue from regional malls and access to jobs. Berks, Columbia, Allegheny and other Pennsylvania counties all have dying malls in 2018 and have per capita incomes less than $29,000.
The labor force participation rate decreased by more than three percentage points from 2000 to 2015. While unemployment rates remain low, fewer workers will have to support a growing retired population in the future. At the same time when other emerging employment opportunities in the gig economy have a technological timestamp, the transformation of the American mall is more than just the end of food courts and your local department store, but also provides insight into the changing nature of work, income, and consumer behavior in the US.