In the past 15 years the neighborhood of downtown Los Angeles has seen a dramatic rise in the number of businesses that have decided to open up shop downtown. But what is driving this dramatic rise in demand for businesses to open downtown? Definite signs of gentrification have been seen, and the catalyst of this movement is in large part due to the creation of the Staples Center in 1998. According the official Staples Center website, this multi-purpose stadium hosts over 250 events and around 4 million visitors a year, an outstanding number of people to see the revitalized downtown neighborhood. Before the completion of the arena, downtown was best known for the juxtaposition of skid row and financial businesses in the financial district. In the early 1990’s, banks located in downtown began to consolidate and merge their offices, thus creating empty office buildings and spaces throughout the neighborhood.
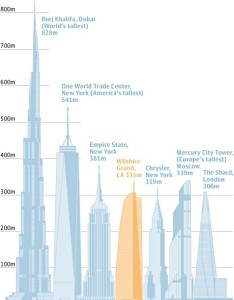
Los Angeles is a city that, despite the economic woes of its state, can be seen as a beacon of hope with a global interest. This sentiment has become increasingly more evident with the construction of the Wilshire Grand building that is owned by Korean Airlines. The Wilshire Grand building will become the eighth largest building in the United States, once completed. And as an economic indicator of a city, the more skyscrapers and tall buildings a city has, the healthier its economy is. That is not always true, but in this case it demonstrates that Los Angeles, and the booming downtown, want to compete on a global scale. Sure, the rebuilding of the downtown neighborhood has been a slow process since the late 1990’s, however, according to Nate Berg, “many in the city are hopeful that the Wilshire Grand is part of a new wave of investment downtown that will help the city compete internationally” (Nate Berg, The Guardian). It seems as though Nate’s sentiments are justified in terms of the investments being brought to the neighborhood, when there are plans for chains like Whole Foods, retailers like Urban Outfitters, and several local restaurants who have decided to expand to the downtown area.
In order to put the rise of downtown in the context of data, towards the end of 2013, “Six parking lots in downtown Los Angeles recently sold for $82 million” according to Dawn Wotapka of the Wall Street Journal. A staggering amount of money for some parking lots that have plans to be turned into an apartment complex. This is just one deal of many that have transpired over the past 15 years, and the figures seem to keep rising.
However, the other side of this story is the issue with occupancy rates, and whether or not there are too few apartments or too many people. Wotapka reports that “With more people flocking downtown, the vacancy rate for apartments has fallen. In the third quarter, downtown Los Angeles had a vacancy rate of 3%, down from 3.3%” Along with the dropping vacancy rates in downtown, which means in increase in demand, the consequence is that the average price of rent jumped almost 4% in the final quarter of 2013.
To shed more light and data on the rise of housing in downtown, Wotanka found “There are about 14,000 apartment units in downtown Los Angeles. About 5,100 units are under construction, and more than 3,400 units were built between 2008 and 2013, according to Polaris Pacific, a real-estate sales, marketing and research firm. More than 3,000 additional rental units have been approved, with another 7,000 proposed. Meanwhile, there are only 17 condo units for sale and 68 under construction.”
Although there are some concerns that there has been such a vast amount of investment for housing downtown that we could see a drop in prices, the consensus among real-estate executives is that the demand will still stay fairly constant and strong. This prediction is justified by a recent report on the diminishing availability of apartment buildings and the relationship with rent prices. Since 2010, rent in the downtown neighborhood has increased by an outstanding 18.2% and is still predicted to grow because of the strong demand.
Another major indicator of the downtown area boom, although it may seem trivial at first glance, is the addition of Whole Foods to the flourishing neighborhood. The development of a Whole Foods in downtown serves not only high-priced, fair trade organic groceries, but as a symbol of the seriousness of downtown as a vital area in Los Angeles. As David Pierson of the Los Angeles Times reports, he calls it “a major development in the neighborhood’s gentrification efforts.” He is not the only one praising the development of the high end grocery store with City Councilman Jose Huizar recently stated “”Downtown Los Angeles is like a city within the city that needs a diverse range of services – including grocery stores,” Huizar said in a statement. “Bringing Whole Foods Market to downtown is long-awaited news that represents a major coup.”
But Whole Foods is not the only tremendously successful chain that has chosen to explore the downtown area, the recently remodeled United Artists Building now called the hip Ace Hotel provides another example of what downtown has become. With locations in London, New York, and Panama to name a few, the expansion to the downtown area exemplifies the “hip” and “young” vibe that the area now exudes.
Downtown has made tremendous strides and has hurdled many obstacles to get the state that it is in today, and many real estate executives believe that the best has yet to come for this burgeoning neighborhood. With rising rents and diminishing vacancy rates, an interesting few years are expected to come in the housing market, with several apartment complexes to be completed. However, in retrospect, you have to look back to the addition of the Staples Center and the subsequent development of L.A. Live as the genesis of this downtown explosion.
Sources: http://www.theguardian.com/cities/2014/feb/14/world-largest-concrete-pour-la-trucks-los-angeles, http://www.aegworldwide.com/facilities/arenas/staplescenter, http://online.wsj.com/news/articles/SB10001424052702304281004579220210670242326, http://articles.latimes.com/2013/jul/31/business/la-fi-mo-whole-foods-downtown-20130731,