The Big Mac index was invented as a lighthearted guide to whether currencies are at their “correct” level. Based on the theory of purchasing-power parity (PPP), the index follows the notion that in the long run exchange rates should move towards the rate that would equalise the prices of an identical basket of goods and services (in this case, a burger) in any two countries.
The Big Mac index was invented as a lighthearted guide to whether currencies are at their “correct” level. Based on the theory of purchasing-power parity (PPP), the index follows the notion that in the long run exchange rates should move towards the rate that would equalise the prices of an identical basket of goods and services (in this case, a burger) in any two countries.
Drawing on the example from the The Economist, the average price of a Big Mac in America in July 2015 was $4.79; in China it was only $2.74 at market exchange rates. So the “raw” Big Mac index says that the yuan was undervalued by 43% at that time.
Never intended to be a precise gauge of currency misalignment, the Big Mac Index has announced itself as a global standard for countries to position themselves in the world through the value of their currency. This could bring some joy to the office of the new CEO of McDonald’s following the fall in revenue by 11% in the last quarter.
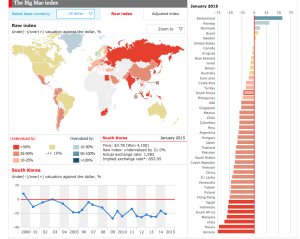
The figure above provides a detailed summary of the Big Mac Index. For example, South Korea, which lost its value against the dollar post 2000 has been on a downward trend and has been significantly devaluaed to 21%. So what does this mean? Well, devaluing the currency decreases the exchange rate of the South Korean Won against the dollar. Hence one dollar can now buy more of the Won. This has a direct impact on the both the economies. It would decrease the value of South Korean goods, making them competitive in the international market, increasing exports from the country and increasing imports in the United States, and worldwide. Simultaneously purchase of foreign goods is more expensive decreasing exports in South Korea. This directly sponsors growth in the economy through increase in net exports. This practice seems relevant to economies that are looking towards growth, for example developing countries. Hence through the chart we can confirm that Russia, India, China and South Africa, four of BRICS countries are focused on aggressive growth. Yes, from the looks of it even China.
For individuals like me, who come from India and other Asian countries to United States, we will have more of currency shock than culture shock. With 1$ woth Rs.66, I am having trouble managing my expenses, so good luck to those students coming to United States for studies. For now, I am considering on going back to India and saving on those precious dollars.
Sources:
http://www.economist.com/content/big-mac-index
http://bigmacindex.org/